13+ Second Order Integrated Rate Law Example
Second Order Integrated Rate Law Example. The two examples given above are the second order reactions depending on the concentration of two separate first order reactants. Other 2 nd order rate laws are a little bit trickier to integrate, as the integration depends on the actual stoichiometry of the reaction being investigated.

Thus, the graph of the second order integrated rate law is a straight. The equation for the second order integrated rate law takes the form y = mx +b, where y = 1/a; Differential and integrated rate equation for second order reactions
roxana vancea instagram salle a manger ikea maroc prix schema branchement jour nuit chauffe eau rouleau isolant thermique aluminium
2c4h6(g)→ c8h12(g) 2c 4 h 6 ( g) → c 8 h 12 ( g) the reaction is second order with a rate constant equal to 5.76 × 10 −2 l/mol/min under certain conditions. (2no_{2} \rightarrow 2no + o_{2}) (2hi \rightarrow i_{2} + h_{2}) these reactions involve one second order reactant yielding the product. The order of the differential rate equation, of course, determines the form of the integrated equation. (k = slope of line) examples.

2.0 × 10 −13 m; Because this equation has the form y = mx + b, a plot of the inverse of [a] as a function of time yields a straight line. Integrated rate law [a] = −kt + [a] 0: For example, an integrated rate law helps determine the length of time a radioactive material must be stored for.

The rate law for a reaction is a useful way of probing the mechanism of a chemical reaction but it isn't very useful for predicting how much reactant remains in solution or how much product has been formed in a. 1 [a] = kt+ 1 [a]0 y = mx+b 1 [ a] = k t + 1 [ a] 0.

Second order reactions ( j=2) the differential form of the rate law is: 2.0 × 10 −13 m; For a first order reaction: How long does it take? 2a products or a + b products (when [a] = [b]) , rate = k[a] 2 the integrated rate law is 1/[a] = kt + 1/[a o] top.

For a first order reaction: If the initial concentration of butadiene is 0.200 m, what is the concentration remaining after 10.0 min? The rate law for a reaction is a useful way of probing the mechanism of a chemical reaction but it isn't very useful for predicting how much reactant remains in solution or how much product has been formed.

Other graphs are curved for azero order reaction. For a first order reaction: If the initial concentration of butadiene is 0.200 m, what is the concentration remaining after 10.0 min? For example, an integrated rate law helps determine the length of time a radioactive material must be stored for its radioactivity to decay to a safe level. The reaction is.

Thus, the graph of the second order integrated rate law is a straight. [\ce{2c4h6}(g) \ce{c8h12(g)} ] the reaction is second order with a rate constant equal to 5.76 × 10 −2 l/mol/min under certain conditions. The reaction of butadiene gas (c 4 h 6) with itself produces c 8 h 12 gas as follows: (2no_{2} \rightarrow 2no + o_{2}) (2hi.
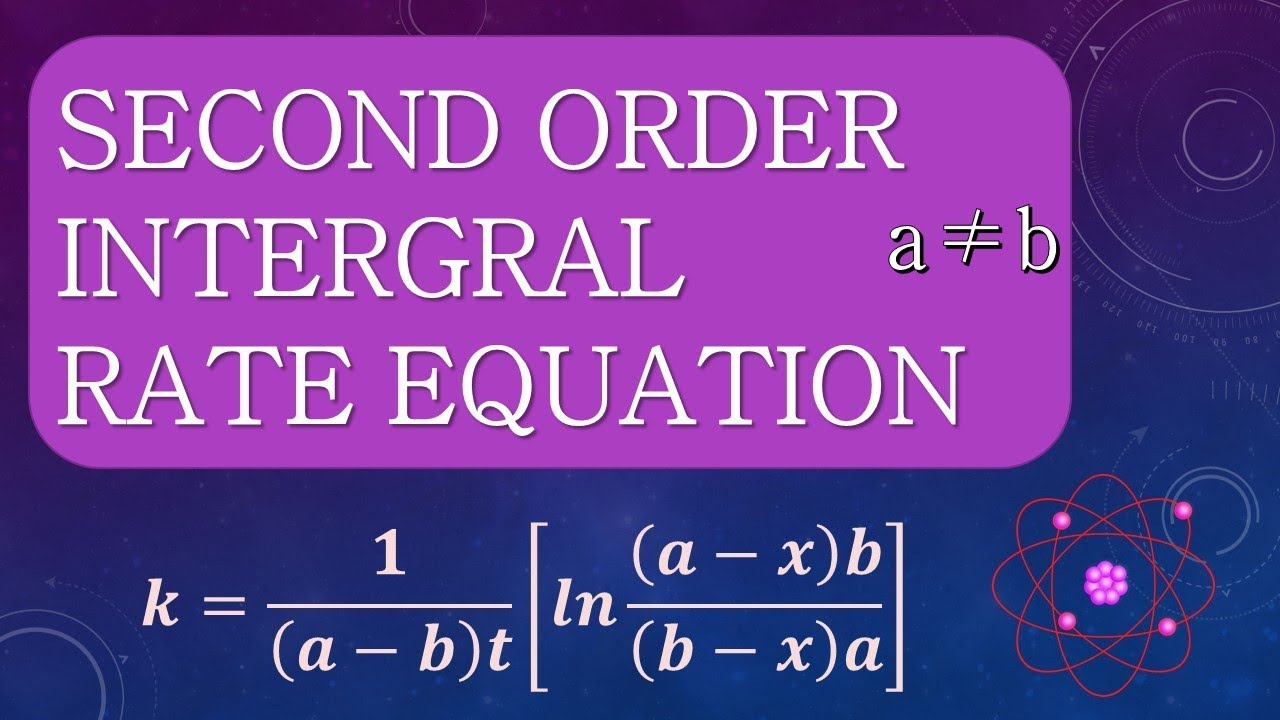
Second order reactions ( j=2) the differential form of the rate law is: Other graphs are curved for azero order reaction. 2a products or a + b products (when [a] = [b]) , rate = k[a] 2 the integrated rate law is 1/[a] = kt + 1/[a o] top. Other 2 nd order rate laws are a little bit trickier.